A New Ebola Vaccine: ExcellGene in a Euro-Swiss Initiative
Author

Florian M. Wurm
PhD, Prof. Emeri.
18th October 2018
The repeated Ebola virus outbreaks in West Africa have reached historic proportions and underscore the vulnerability of populations to pathogens. Outbreaks of infection by the Zaire Ebola virus have been characterized by greater breadth and more rapid spread. While an experimental virus-vector based vaccine has been used for the first time recently, the data gained are not sufficient to assume its’ effectiveness. In fact, no vaccines are approved for prevention of Ebola infections today. Thus, an effective vaccine is still needed to protect healthcare workers and exposed populations, especially those operating and living in poor field conditions.
The (European Union's EU-H2020 IMI-program) and Switzerland (Swiss Secretary of State for Education, Research and Innovation) agreed to partially fund an innovative research project, initiated by Vaxeal Holding SA, Switzerland, to develop a recombinant protein/peptide-based vaccine for the prevention of EBOLA infections in humans. The total investment accounts for an estimated sum of 18 Mio Euro. The innovative approach is based on the use of two complementary and synergistic components – proteins and peptides. The vaccine candidate will be prepared by combining a variant of the glycoprotein of the surface of the virus (GP) (proteins that “decorate” the outer surface of the virus) and peptides derived from the nucleoprotein (NP) (another protein that is located inside of the virus particle).
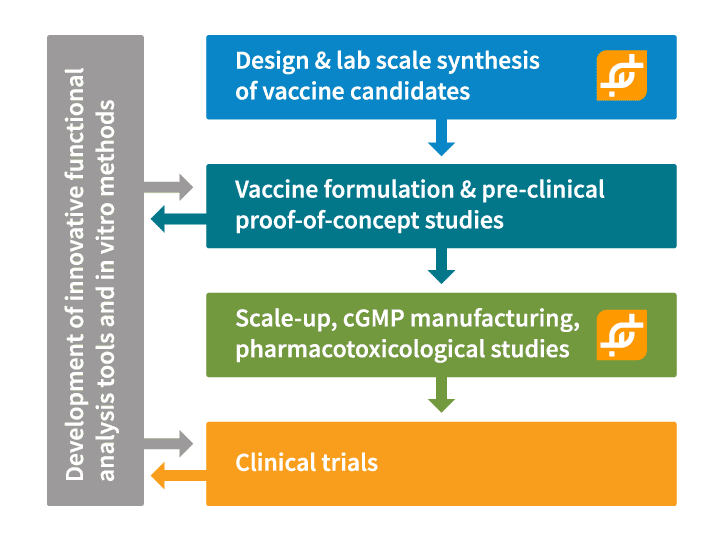
Thus, the Pan-Ebola Vaccine Innovative Approach (PEVIA), planned and executed by 13 international partners, including two R&D partners from Switzerland - ExcellGene and the Cantonal University Hospital of Vaud (CHUV, Group F. Spertini) - intends to bring to clinical trials in Europe and Africa a “subunit, prime-boost” vaccine, without the use of any virus particles. The PEVIA consortium aims to provide a preventive vaccine, safe and effective against multiple Ebola virus strains and readily deployable in endemic regions. The vaccine shall be formulated and distributed in a form that would not require expensive and complex “cold-chain” transport and ultra-low temperature storage conditions.
Understanding the importance of the Ebola vaccine initiative, ExcellGene is honored to contribute to the identification, design and lab-scale synthesis of highly immunogenic, soluble glycoprotein variants and, eventually, the development of a high-yielding manufacturing process for the best candidate molecules. ExcellGene will also be responsible for the manufacturing of clinical-grade preparations of this unique, highly pure GP variant protein.
Discover more about the PEVIA Ebola vaccine project.


This project has received funding from the Innovative Medicines Initiative 2 Joint Undertaking under grant agreement No 116088. This Joint Undertaking receives support from the European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme, and EFPIA.